BLOG POST
The future of the German economy: Will robots help to combat the shortage of skilled workers?
In today’s globalized economy, Germany, like many other contries, faces one of the greatest challenges of the 21st century: the shortage of skilled workers. This problematic situation affects almost all industries and threatens the countries’ economic growth and innovative strength. One solution for the industry may be the use of robots. But how effective is this approach and what are the effects of the shortage of skilled workers? And how will robots help to address the shortage of skilled workers?
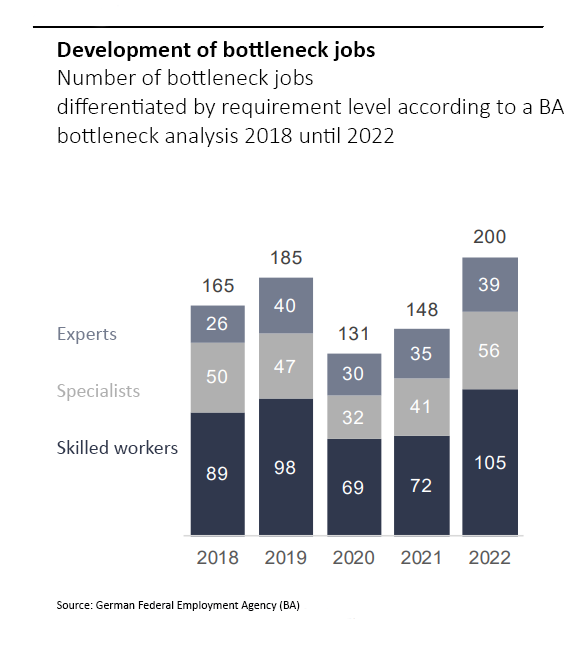
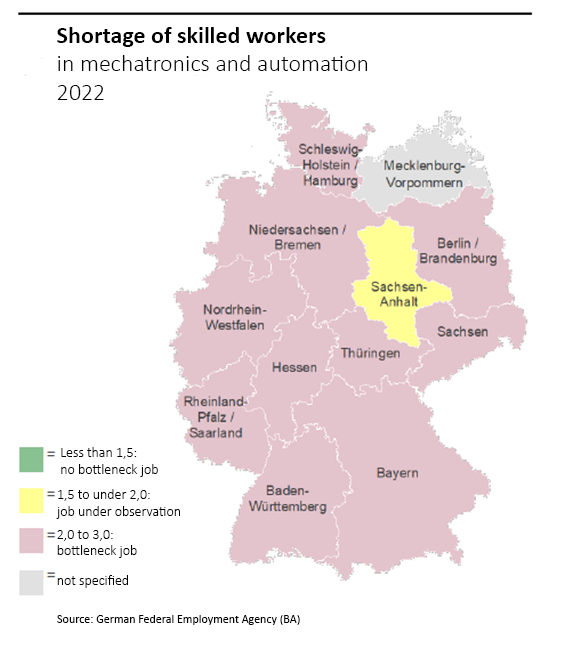
Figure 1 from the German Federal Employment Agency makes it clear: Germany needs more skilled workers. The figures are expected to deteriorate further in the current year (2023). Figure 2 shows the problem specifically with regard to skilled workers in the field of mechatronics and automation. So to speak they are nationwide among the bottleneck occupations. And German industrial companies are clearly feeling the resulting consequences.
The shortage of skilled workers: a serious problem
The shortage of skilled workers has become a burning issue in recent years – also in Germany. As figure 2 shows, this problem is particularly pronounced in technical and engineering professions and is therefore of great importance in the industrial and manufacturing environment. There are many reasons for the shortage of workers:
Demographic change: Germany is experiencing an aging population, resulting in many experienced professionals retiring and fewer young people entering the labor market. Baby boomers in particular will retire in the next few years, leaving a significant gap.
Education system: Demand for qualified workers often exceeds supply. This is partly due to challenges in the German education system and the training of skilled workers, but also to a lack of attractive training opportunities on the labor market.
Competition from abroad: Today, skilled workers have the opportunity to search globally for the best job opportunities. This leads to increased competition for talent.
The consequences for the German economy
Production delays: In industry, the lack of qualified employees leads to production delays and rising costs.
Innovation lack: Without sufficient skilled personnel, German companies fall behind when it comes to developing and implementing innovative technologies.
Brake on growth: Germany is competing internationally for investment and orders. A lack of skilled workers reduces productivity and jeopardizes competitiveness..
Industries particularly affected
In the industrial sector, almost all industries are affected by the shortage of skilled workers. However, one sector in particular is struggling: the automotive and supplier industry. One of the largest pillars of the German economy is trying to remain competitive in international comparison: Digitalization instead of mechanics. Topics that currently seem utopian or far off in the future are becoming increasingly relevant, such as autonomous driving or innovative drive types.
One of the biggest competitors in this market is China, which offers lower-quality but lower-cost alternatives. The response from Germany’s largest automotive company VW was clear: in 2022, 18.9 billion euros were spent on research and development (R&D).
But for this spending to have an impact, expert personnel are needed who see digitization and automation as an opportunity rather than a threat.
Robotics as part of the solution
How can robotics help here? The use of industrial robots and cobots opens up opportunities to create free space for employees and provide relief.. Employees then have the time to pursue other, more highly skilled tasks or to continue and deepen their education. Particularly physically demanding or repetitive work can be optimally taken over by robots.
However, this approach is often not pursued further because companies usually associate high integration and training costs with the use of robots, as well as specialist expertise due to the individual robot programming languages. But in this context, there are template-based and manufacturer-independent programming tools such as ArtiMinds RPS that make it easier for companies to integrate and operate robots to ensure economical and efficient deployment.
Expert knowledge in robot programming becomes superfluous, the process expert can become a robotics expert without prior knowledge. The use of industrial robots can thus help solve the problem of the shortage of skilled workers and maintain the competitiveness of the German economy. Which aspects play a special role here?
Increased efficiency: Robots can take over repetitive and hazardous tasks in production, which increases company productivity, relieves human labor and frees up additional capacity.
Quality control: Robots are able to perform precision work while maintaining high quality, reducing errors, scrap and costs.
Flexibility: Modern industrial robots are versatile and flexible and can perform a wide range of tasks and processes. Thanks to low-code tools such as ArtiMinds RPS, it is quick and easy to adapt the robot or the programmed process for new requirements and work steps, allowing you to respond to small batch sizes or fluctuating demand, for example.
Savings: In the long term, investments in robotics can reduce costs and help offset skill shortages.
Attractive jobs: New and advanced technologies make employers and jobs more attractive in the long run and can tip the scales in a highly competitive labor market. They also open up new opportunities for innovation and new business models.
The more robots, the more jobs?
What sounds contradictory at first could actually be true! In times of Industry 4.0, a change in thinking must occur in people’s minds. At first glance, robots and the automation of business or production processes pose a kind of threat to people’s own jobs, but according to KUKA manager Heinrich Munz, the opposite is true: digitalization and automation obviously create jobs.
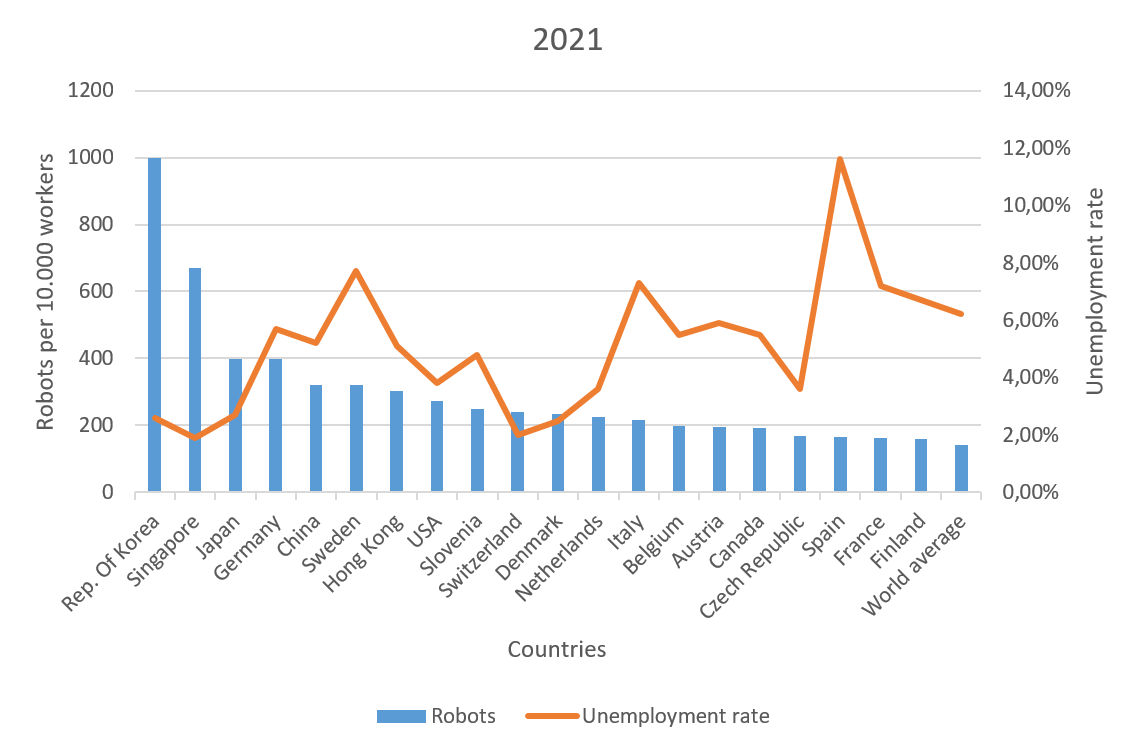
If you compare the number of industrial robots installed with the unemployment rate, a clear trend emerges. Countries that are at the forefront of robotization have a lower unemployment rate (see figure 3). This is primarily due to the fact that although robots can perfectly take on simple or mechanical tasks, humans are still needed to perform more complex or creative tasks. In other words, while simple or monotonous tasks are being eliminated, new occupational fields are emerging around the development, programming and use of robots.
Conclusion
The shortage of skilled workers is undoubtedly a major challenge for economic policy – and not just in Germany. However, a combination of measures is needed to address this problem.
The automation and integration of robots into industrial (manufacturing) processes is a good approach to increase efficiency, reduce costs and maintain the competitiveness of countries in the global economy. However, robotization is also associated with challenges. This is because it requires investment in robot technologies, training, creating an environment in which humans and machines can work together harmoniously and, above all, rethinking and a willingness to change.
No-code and low-code solutions such as ArtiMinds RPS or ArtiMinds LAR, which facilitate the programming of robots, analyze processes in an automated manner and thus also make it possible to automate more complex tasks, open up new fields of application, reduce the amount of training required and increase the flexibility and innovative strength of companies.
With this white paper, we want to provide you with guidance for your automation plans. To help you to avoid typical pitfalls when using robots, we highlight the top 5 underestimated challenges and stumbling blocks when getting started in robotics and provide you with helpful tips and interactive checklists.
Program and simulate robot applications independent of manufacturers, reduce maintenance costs and alleviate the lack of skilled workforces. Find out how ZF succeeds thanks to ArtiMinds!
MUCH MORE THAN JUST SIMPLE ROBOT PROGRAMMING: With RPS you create cross-process standardization – from planning and programming to maintenance.